Let’s explore the fascinating world of smart appliances and delve into the important topic of security risks. In this article, we will take a closer look at the potential vulnerabilities that come with these connected devices. From smart refrigerators to voice-assistant-enabled thermostats, we will discuss the security considerations that should be on your radar. So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on this enlightening journey to better understand the security risks of smart appliances.
Understanding the Security Risks of Smart Appliances
Overview of Smart Appliances
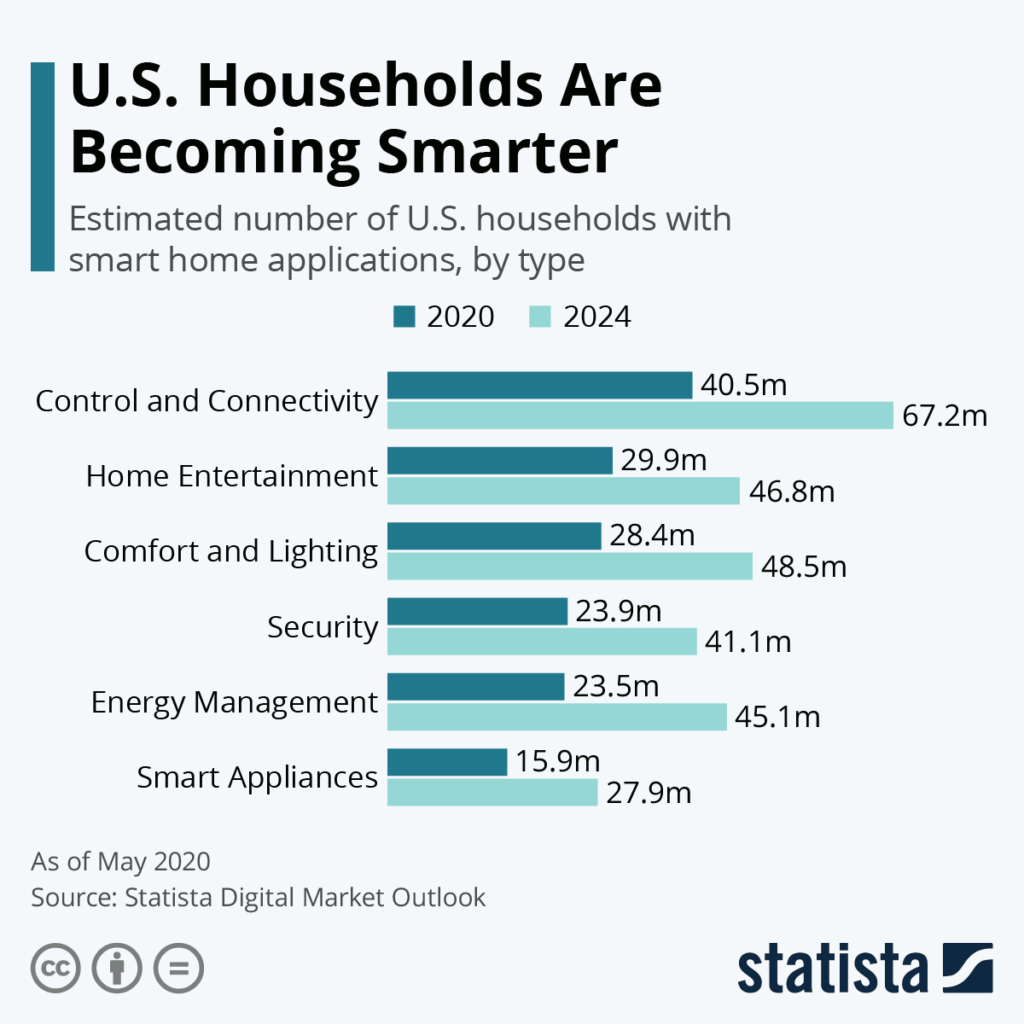
Smart appliances, also known as connected appliances, are household devices that can connect to the internet and be controlled remotely. They provide convenience and automation in various aspects of our daily lives, such as cooking, cleaning, and energy management. Examples of smart appliances include smart refrigerators, ovens, washing machines, thermostats, and security systems. These appliances are designed to enhance efficiency, save energy, and improve user experience.
Growing Threat Landscape
With the rapid adoption of smart appliances, the threat landscape is also expanding. Hackers and cybercriminals are continuously evolving their strategies to target vulnerabilities in smart homes. The increasing number of internet-connected devices provides more entry points for cyberattacks. Malicious actors can exploit loopholes in security protocols, gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data or even taking control of smart appliances. It is crucial to understand and address these security risks to protect our smart homes and ensure the safety of our personal information.

This image is property of assets.entrepreneur.com.
Lack of Industry Standards
One of the major challenges in securing smart appliances is the absence of uniform security guidelines across the industry. Unlike well-established standards for traditional household appliances, the security measures for smart appliances vary significantly. Each manufacturer implements their own security protocols, resulting in inconsistencies and potential vulnerabilities. This lack of industry standards makes it difficult for consumers to assess the security of smart appliances and choose products that adequately protect their privacy and safety.
Inadequate Authentication Mechanisms
Authentication is a key component of ensuring the security of smart appliances. Unfortunately, many smart appliances suffer from inadequate authentication mechanisms. Weak or default passwords are often used by manufacturers, making it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access. Furthermore, the lack of two-factor authentication (2FA) leaves smart appliances vulnerable to password attacks. Insufficient user access controls also contribute to the risks, as multiple users may have access to the same device, increasing the likelihood of unauthorized access.

This image is property of www.firstrepublic.com.
Vulnerabilities in Communication Protocols
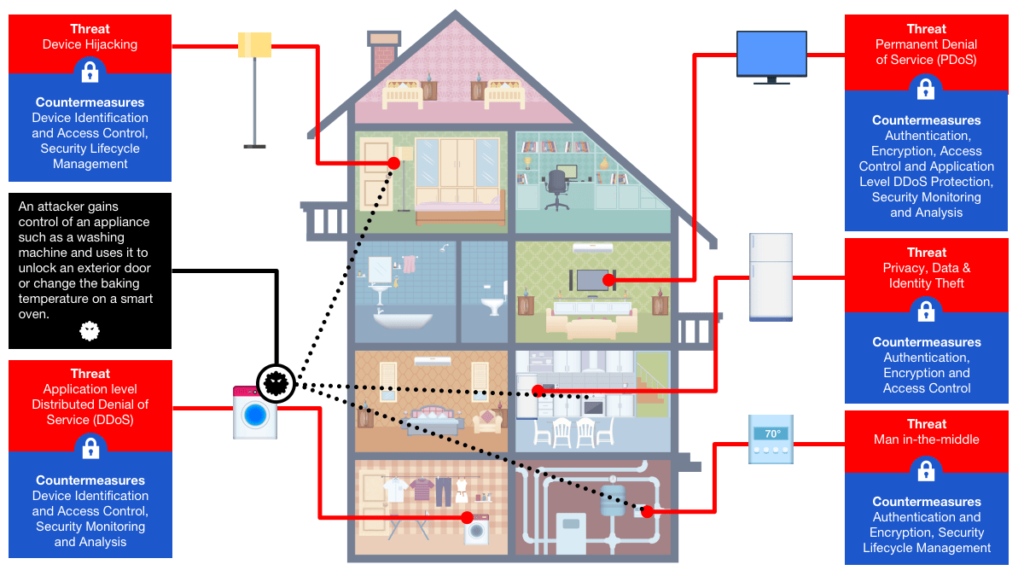
Smart appliances rely on various communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee, to connect to the internet and communicate with other devices. However, these protocols can be vulnerable to attacks. Insecure Wi-Fi networks can be easily breached, allowing hackers to intercept sensitive data or gain access to connected appliances. Flaws in Bluetooth and Zigbee protocols can also be exploited, enabling unauthorized control or manipulation of smart appliances. Man-in-the-Middle attacks, where hackers intercept and alter communication between devices, pose a significant threat to the security of smart appliances.
Data Privacy Concerns
The collection of sensitive data is a common feature in smart appliances. These devices often gather information about user habits, preferences, and usage patterns to optimize their functionalities. However, this collection of sensitive data raises significant privacy concerns. If not adequately protected, this data can be compromised, leading to unauthorized access or data breaches. Hackers targeting smart appliances may leverage the collected data for malicious purposes, such as identity theft or targeted attacks. It is vital for manufacturers to implement robust security measures to safeguard user data and maintain user privacy.
This image is property of www.rambus.com.
Potential for Physical Attacks
While cyberattacks are the primary concern when it comes to smart appliances, there is also a potential for physical attacks. Malware specifically designed for smart appliances can cause malfunctions or damage to the devices. Hackers may manipulate the physical controls of smart appliances remotely, leading to safety risks or sabotaging their functionalities. These physical attacks can have serious consequences, jeopardizing the safety and well-being of individuals within the household.
Risks of Third-Party Integrations
Smart appliances often integrate with third-party applications and devices, such as voice assistants or home automation systems. While these integrations provide enhanced functionality and convenience, they also introduce additional security risks. The security of these third-party apps and devices may not be as robust as the smart appliances themselves, creating vulnerabilities for attackers to exploit. The more integrations a smart appliance has, the larger its attack surface becomes, increasing the risk of unauthorized access or control by cybercriminals.
This image is property of assets.weforum.org.
Lack of Regular Software Updates
Regular software updates play a vital role in addressing security vulnerabilities and protecting smart appliances from emerging threats. Unfortunately, many manufacturers fail to provide timely updates or end-of-life support for their products. This lack of regular software updates leaves smart appliances running outdated and insecure software, making them susceptible to known vulnerabilities. It is essential for consumers to choose smart appliances from manufacturers committed to providing regular updates and security patches to ensure the longevity and security of their devices.
Security Risks and Smart Home Networks
Smart appliances are part of a larger ecosystem within smart home networks. This interconnectedness creates both opportunities and challenges in terms of security. Compromised devices within the network can act as entry points for attackers, potentially compromising the entire network and all connected devices. A single vulnerable smart appliance can expose sensitive data or allow unauthorized control over other devices. It is crucial to implement comprehensive security measures, including network segmentation, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, to protect smart home networks from potential security risks.
In conclusion, while smart appliances offer numerous benefits and convenience, they also introduce security risks that must be understood and addressed. The lack of industry standards, inadequate authentication mechanisms, vulnerabilities in communication protocols, data privacy concerns, potential for physical attacks, risks of third-party integrations, lack of regular software updates, and the impact on smart home networks all contribute to the security risks associated with smart appliances. It is essential for consumers to be aware of these risks and take proactive measures to protect their smart homes and personal information. By choosing reputable manufacturers, implementing strong authentication measures, keeping software up to date, and securing smart home networks, you can enjoy the benefits of smart appliances while minimizing the potential security threats they pose.
This image is property of cdn.nextgov.com.





