Imagine living in a world where your home is always connected, where your devices seamlessly communicate with each other, making your life easier and more convenient. But with so many smart devices on the market, it’s important to understand the difference between technologies like Wi-Fi and Zigbee/Z-Wave. While both allow for wireless communication, each has its own unique characteristics and use cases. In this article, we’ll explore the distinctions between Wi-Fi and Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices, helping you make informed decisions when it comes to creating your smart home ecosystem. So, let’s dive into the world of wireless connectivity and explore the fascinating contrasts between these two popular technologies.
Wi-Fi Smart Devices
Definition
Wi-Fi smart devices are electronic devices that can be connected to a Wi-Fi network and controlled remotely using a smartphone or a computer. These devices utilize Wi-Fi technology to communicate with other devices on the same network, allowing for convenient and seamless control.
Technology
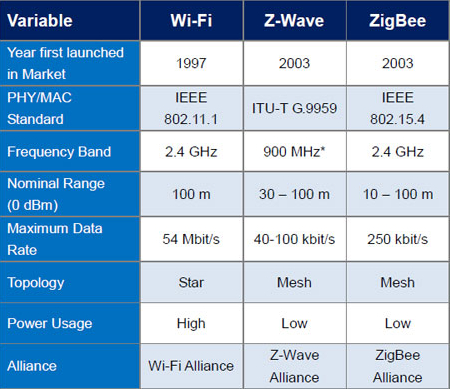
Wi-Fi smart devices use the same Wi-Fi technology that is commonly found in most homes and offices. They connect to the local Wi-Fi network, enabling communication between the device itself and the controlling device, such as a smartphone or a computer. This technology allows for a wide range of functionalities and features, making Wi-Fi smart devices versatile and user-friendly.
Range
The range of Wi-Fi smart devices largely depends on the range of the Wi-Fi network they are connected to. In most cases, the range of Wi-Fi networks is sufficient for controlling devices within a home or office. However, it is important to note that factors such as walls, distance, and obstacles can affect the range and signal strength of the Wi-Fi connection.
Power Consumption
Wi-Fi smart devices typically require a constant power source in order to function properly. Since they are constantly connected to the Wi-Fi network and are designed to be accessible at all times, they consume electricity even when not in use. It is recommended to connect these devices to a power source that allows for efficient power management, such as smart power outlets or power strips with energy-saving features.
Interference
Interference can be a concern with Wi-Fi smart devices, especially in areas with a high density of Wi-Fi networks or other wireless devices. Interference from other networks or devices operating on the same frequency can degrade the performance and reliability of Wi-Fi smart devices. However, modern Wi-Fi routers and devices are equipped with advanced technologies to mitigate interference and ensure smooth and uninterrupted communication.
Set-up
Setting up Wi-Fi smart devices usually involves a few simple steps. First, the device needs to be connected to a power source. Then, the device is connected to the Wi-Fi network through a mobile app or a web interface. During the set-up process, the device may require some initial configuration or pairing with the controlling device. Once the set-up is complete, the device can be controlled remotely using a smartphone or a computer.
Compatibility
Wi-Fi smart devices are generally compatible with a wide range of Wi-Fi networks, making them versatile and easy to integrate into existing setups. As long as the network meets the required specifications, such as the Wi-Fi frequency and security protocols, Wi-Fi smart devices can be connected and controlled seamlessly. It is important to check the compatibility requirements of the specific device before purchasing, as some devices might have specific compatibility limitations.
Security
Security is a crucial aspect to consider when using Wi-Fi smart devices. Since these devices are connected to the internet, they can be vulnerable to cyber attacks if not properly secured. It is recommended to use strong, unique passwords for Wi-Fi networks and smart device accounts. Additionally, keeping devices and software up to date with the latest security patches and using reputable brands and manufacturers can help ensure a higher level of security.
Cost
The cost of Wi-Fi smart devices can vary depending on the brand, functionality, and features. Generally, Wi-Fi smart devices are more widely available and tend to have a wider range of options compared to other smart device technologies. This means that there are more affordable options available for those on a budget, as well as higher-end options with advanced features that come at a higher price point. It is important to consider the value and long-term savings that smart devices can provide when assessing the cost.
Popular Wi-Fi Smart Devices
Some popular Wi-Fi smart devices on the market include smart thermostats, smart cameras, smart light bulbs, smart plugs, and smart speakers. These devices offer enhanced convenience, energy efficiency, and home automation capabilities. Brands such as Google Nest, Amazon Echo, Philips Hue, and TP-Link have gained popularity for their Wi-Fi smart devices, offering a wide range of options to suit different needs and preferences.
Zigbee/Z-Wave Smart Devices
Definition
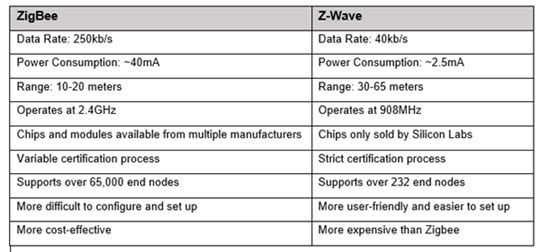
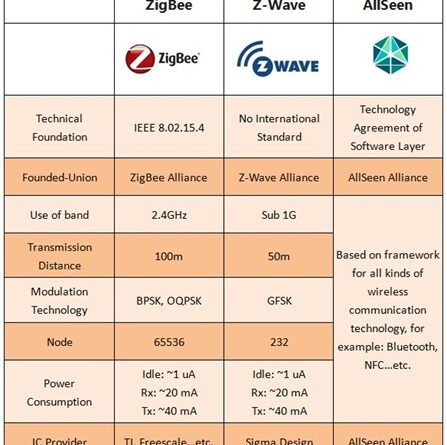
Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices are another category of smart devices that utilize different wireless technologies for communication. Zigbee and Z-Wave are low-power, mesh network technologies that enable devices to communicate with each other, creating a robust and reliable network for smart home automation.
Technology
Unlike Wi-Fi smart devices, Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices use their own dedicated wireless technologies, Zigbee and Z-Wave, respectively. These technologies operate on different frequency bands and utilize mesh network topologies, where multiple devices work together to extend the range and reliability of communication. This makes Zigbee/Z-Wave networks ideal for large homes or areas with multiple smart devices.
Range
Zigbee and Z-Wave smart devices typically have a longer range compared to Wi-Fi smart devices. The mesh network topology allows each device to act as a relay, effectively increasing the coverage area of the network. This enables Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices to communicate with each other even if they are located far away from the central hub or controller.
Power Consumption
One of the key advantages of Zigbee and Z-Wave technologies is their low power consumption. Due to their optimized design and low data transfer rates, Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices can operate on battery power for extended periods of time. This makes them an ideal choice for battery-powered or low-power devices such as sensors, door locks, and thermostats.
Interference
Zigbee and Z-Wave technologies operate on different frequency bands compared to Wi-Fi networks and other wireless devices. This reduces the likelihood of interference and ensures a more reliable and stable communication between Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices. However, it is still possible for other wireless devices operating within the same frequency range to cause interference, although it is less common.
Set-up
Setting up Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices typically involves connecting a central hub or controller to the existing Wi-Fi network. Once the hub is connected, devices can be added to the network by following the manufacturer’s instructions. Most Zigbee/Z-Wave devices require the hub to be within close proximity during the initial set-up process. After the set-up is complete, the devices can be controlled and monitored remotely using a smartphone or a computer.
Compatibility
Zigbee and Z-Wave smart devices are designed to be compatible with each other, creating an open ecosystem where devices from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly. This allows users to mix and match devices from various brands without worrying about compatibility issues. However, it is still important to check the compatibility requirements of each device to ensure proper integration with the chosen hub or controller.
Security
Similar to Wi-Fi smart devices, security measures should be taken to ensure the safety of Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices. These technologies implement their own encryption mechanisms to protect the communication between devices, providing a certain level of security. However, as with any smart device, it is important to regularly update firmware and use strong passwords to mitigate security risks.
Cost
Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices are available at various price points, depending on the brand, functionality, and features. While the initial cost of setting up a Zigbee/Z-Wave network might be higher compared to Wi-Fi smart devices, the long-term benefits and scalability make them an attractive option for those looking to expand their smart home automation capabilities. It is important to consider the long-term value and potential savings that Zigbee/Z-Wave networks can provide.
Popular Zigbee/Z-Wave Smart Devices
Popular Zigbee/Z-Wave smart devices include smart door locks, motion sensors, temperature sensors, smart light switches, and smart window blinds. Brands such as Samsung SmartThings, Philips Hue, and Aeotec offer a wide range of Zigbee/Z-Wave devices that can seamlessly integrate into a Zigbee/Z-Wave network. These devices are known for their reliability, compatibility, and ability to create a comprehensive smart home automation system.